Impeccable origin


Diamond Cut Guide: Understanding Cut Grade & Quality
Alicia Briggs and Kimberly Zerkel | August 16, 2023
Of the diamond 4Cs, diamond cut will have the greatest impact on a diamond’s overall beauty and value. A high-quality cut invites maximum light for breathtaking brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Diamond cut influences how large, brilliant, and lustrous your diamond appears. It can make a lower-color-grade lab-grown diamond shine brighter or cause a nearly-flawless diamond to appear dull.
But choosing the right diamond cut for your preferred diamond can sometimes feel overwhelming. Use this diamond cut guide to learn what diamond cut means and how to select the best diamond cut grade and type for you.
What Is Diamond Cut?
Diamond cut is one of the 4Cs of diamonds - cut, color, clarity, and carat. Cut refers to the arrangement of a diamond’s facets. It affects the way the diamond’s surface interacts with and catches light and determines its overall brilliance.
Diamond cut includes cut quality and cut type. There are three types of diamond cuts: step cut, brilliant cut, and mixed cut. Each type of cut, as well as its cut quality, will affect what a diamond looks like and how it plays with the light.
What Are Diamond Facets?
Diamond facets are the flat surfaces inside a diamond that are arranged in a geometrical pattern. Facets affect how a diamond reflects and refracts light but they do not determine its outward shape.
Diamond Cut vs Diamond Shape
Diamond cut often gets confused with diamond shape, but they are two different things. Shape refers to a diamond’s outward, physical form. It’s the most distinguishable feature of a diamond. A diamond’s shape is considered its personality. It often holds symbolic meaning and is a form of self-expression. Examples of diamond shapes include Round Brilliant or Emerald diamonds.
Diamond cut refers to a diamond’s facets, symmetry, and dimensions. It describes the way a diamond reflects light, not how the diamond is outwardly shaped. Emerald and Radiant cut diamonds are a great example of the difference between cut and shape. Both of these diamonds have rectangular shapes, but they feature different cut types. Emeralds have a step-cut with long, linear facets that create a “hall of mirrors” effect when reflecting light. But Radiants have a brilliant cut which resembles crushed ice when reflecting light.
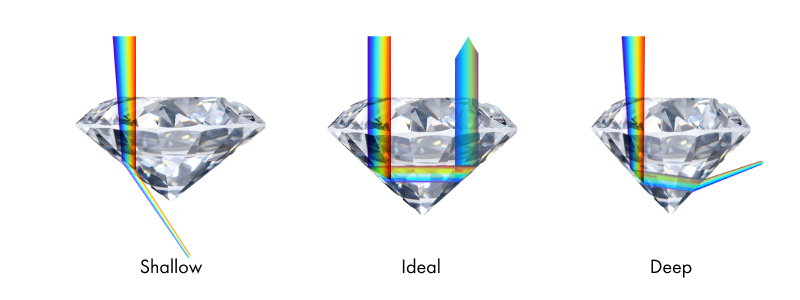

Diamond Cut Grading
To evaluate the quality of a diamond’s cut, a trained gemologist uses diamond grading. They assess how light enters and exits each diamond to determine its cut grade.
What Are Diamond Cut Grades?
Diamond cut grades were established by the GIA to create a universal system for evaluating the cut quality of any diamond.
Gemologists use this system to assign one of five cut grades to a diamond (except for Round Brilliant diamonds which have their own cut grades). Diamond cut grades indicate the quality, not the type, of a diamond cut and will greatly impact the diamond price.
When buying a diamond, always look for a diamond cut grade to ensure its quality.


Be the first to know
Hear about our latest designs and upcoming events.
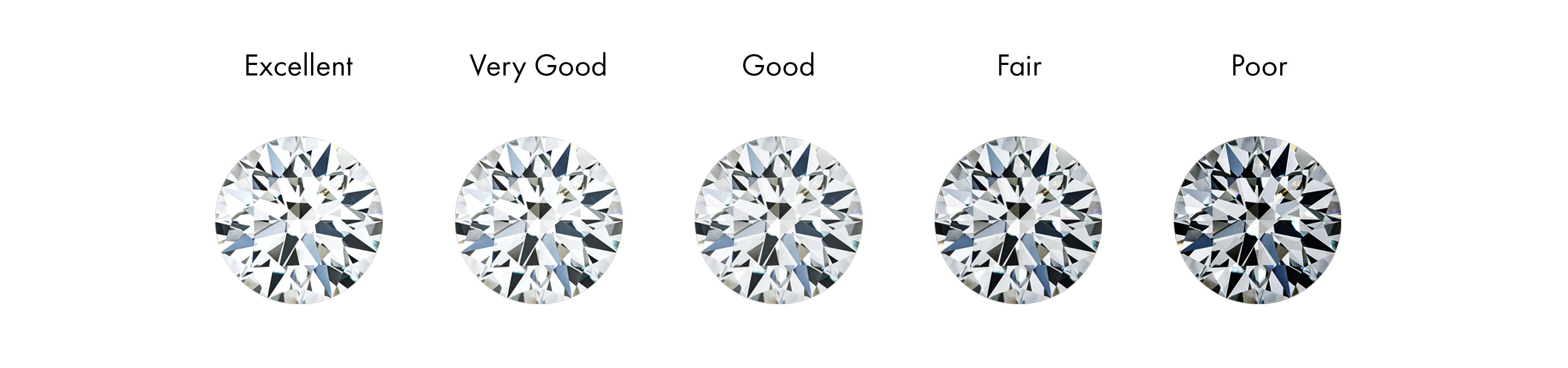
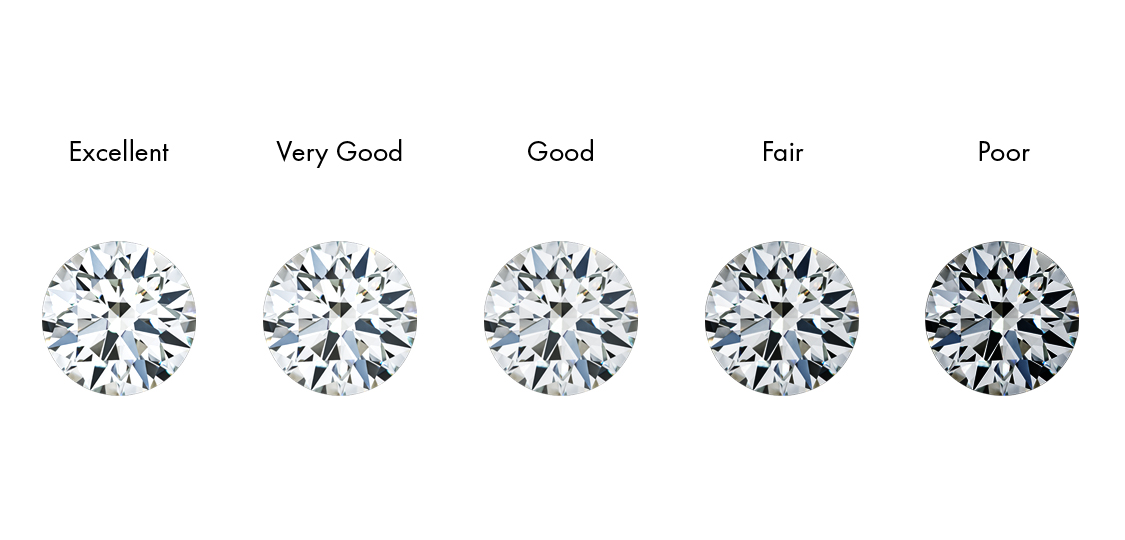
Diamond Cut Grade Chart
Use the chart below to understand the different diamond cut grades.
Ideal+HeartsThis is the top cut grade and is only used for Round Brilliant cut diamonds. It is a superior ideal cut with perfect optical symmetry displaying hearts and arrows-shaped patterns when viewed from the table down and up. Only <1% of all diamonds are Ideal + Hearts.
IdealIdeal is the next highest cut grade reserved for Round Brilliant cut diamonds. Ideal diamonds are cut to maximize brilliance with perfect proportions. This is a rare quality held by <1% of all diamonds.
ExcellentExcellent is the highest cut grade for all diamond shapes outside of Round Brilliants. It’s a perfect premium cut proportioned to return the maximum brilliance possible.
Very GoodA very good cut means that defects are invisible to the naked eye. This can be a wonderful cut grade for shoppers that are prioritizing other Cs or looking for diamonds at a more accessible price point.
GoodGood means that any defects are still invisible to the naked eye. VRAI does not offer diamonds of this cut grade.
FairFair diamonds have defects that may be visible to the naked eye. VRAI does not offer diamonds of this grade.
PoorPoor diamonds have defects that are visible to the naked eye. VRAI does not offer diamonds of this grade.
How Diamond Cut Quality Is Determined
A trained gemologist determines a diamond’s quality of cut based on its brightness, fire, scintillation, and proportions.
The depth, culet, table, and girdle of diamonds with a higher cut quality will be more perfectly proportioned, symmetrical, and polished.
When a diamond’s proportions are cut to exacting precision, light enters and exits the diamond through the same surface (the table). If a diamond’s cut with proportions that are too shallow or deep, light escapes through the bottom or sides of the diamond. This creates less light reflection and a duller appearance.
Here is a breakdown of each factor that a gemologist uses to determine a diamond’s cut grade:
Light
- Brilliance: The total light reflected from a diamond.
- Fire: The dispersion of light into the colors of the spectrum. Color should only appear on the outer edges of a diamond when exposed to light.
- Scintillation: The flashes of white light when a diamond is moved from side to side.
Proportions
- Table: The flat, top surface of the diamond.
- Culet: The small point at the bottom of the diamond pavilion where the facets meet.
- Depth: The distance between the “table” (top of the diamond) and the culet, also known as how “tall” the diamond is.
- Girdle: The outermost edge of a diamond, where the top meets the bottom.
- Precision: How the size and angles relate to the different parts of the diamond.
- Symmetry: How precisely the various facets of a diamond align and intersect.
- Polish: The details and placement of the facet shapes, as well as the outside finish of the diamond.


What Are Different Diamond Cuts?
There are three different types of diamond cuts. Diamond cut type refers to how a diamond is cut i.e. its faceting structure, but not the quality of the cut.
Brilliant Cut
The brilliant cut is composed of triangular and kite-shaped facets spreading outward from the diamond’s center. Brilliant cuts look somewhat similar to crushed ice or a prism when reflecting the light.
They are most commonly used in Round Brilliant cut diamonds but they are also found in other rounder fancy shape diamonds. Cushion, Marquise, Oval, Pear, and Trillion cut diamonds also have brilliant cuts.
Step Cut
The step cut features rectangular facets ascending in size outward and descending in size downward. Each facet is long and linear which creates a distinct “hall of mirrors” effect when reflecting the light. Step cuts are most commonly paired with Emerald, Asscher, and Baguette cut diamonds.
Mixed Cut
The mixed cut is true to its name and is composed of both brilliant and step cut facets. Mixed cuts resemble crushed ice when reflecting the light. They are usually featured in “newer’ diamond shapes, such as Princess, Cushion, and Radiant cut diamonds.
What Is the Best Type of Diamond Cut?
The diamond shape determines the best type of diamond cut, as different cut types work best for specific diamond shapes.
Overall, the best-selling diamond cut and shape is a Round Brilliant cut diamond. True to its name, it often outshines all other diamonds by delivering optimal brilliance, fire, and scintillation. This is why the Round Brilliant cut diamond is the most popular diamond shape in the world.


How to Choose the Best Diamond Cut for You
When it comes time to buy an engagement ring, multiple factors will determine the best diamond cut for you.
First, consider your budget. Diamond cut affects the price of a diamond, as does diamond shape, carat weight, and the engagement ring setting.
Secondly, select your diamond shape. If you have a lower budget, and you’re not set on a specific diamond shape, consider a shape that still looks beautiful at slightly lower cut grades, like an Asscher or Emerald. But for other shapes, like Princess, Radiant, and Round Brilliant diamonds, the cut quality should be prioritized over the other 4Cs.
A VRAI diamond expert can help you work within your budget to find the right balance of cut, color, and clarity grades when buying a diamond.
Diamond Cut FAQs
Here are some answers to the most frequently asked questions about diamond cut and quality.
How Are Diamonds Cut?
A diamond is cut by cleaving or sawing the diamond with a steel blade or a laser. A rough diamond is usually placed inside a mold to hold it in place, then cleaved at its weakest point. If no point of weakness exists, sawing is used instead.
Diamonds are cut and polished by master craftsmen. When a cut is graded by a gemologist, they are essentially evaluating craftsmanship. A skilled diamond cutter will be the difference between a higher or lower cut grade. This factor sets cut apart from clarity and color, which are both naturally occurring.
Which Diamond Cut "Sparkles" the Most?
A Round Brilliant cut diamond is considered the most brilliant — or “sparkliest” — of all diamond cuts.
Brilliant cuts and mixed cuts are generally considered to sparkle the most, whereas step cuts highlight a diamond’s clarity.
What Diamond Cut Looks the Biggest?
Diamond cut will influence how big or small your diamond appears. Diamonds with optimal brilliance tend to appear larger to the naked eye than others similar in shape and carat weight.
Because of this, high-quality Round Brilliant cut diamonds tend to look bigger than they are.
Cut is only one factor that determines the perceived size, however. Diamond shape will play a large role. Diamonds with elongated forms, like Marquise or Oval diamonds, will usually appear larger than a Round Brilliant cut diamond of the same quality and carat weight.
But a poor quality cut will always make a diamond look smaller than its actual carat weight. This is why cut is considered the most important of the 4Cs. Investing in a flawless, colorless, 2-carat diamond, for example, is only worth it if its cut maximizes its brilliance and allows it to shine bright.
What Is the Most Expensive Diamond Cut?
The highest cut grade is Ideal + Hearts for a Round Brilliant cut diamond, and Excellent for other diamond shapes. As such, these are the most expensive diamond cut grades.
Due to its popularity and high demand, a Round Brilliant cut diamond is the most expensive type of diamond cut. Brilliant cuts in general are more expensive than step cut diamonds, depending on the quality of the cut. This is due to both higher demand and differences in the cutting process.
What Are Hearts and Arrows?
Hearts and Arrows only appear in precision-cut Round Brilliant diamonds with an Ideal + Hearts cut grade. When observed through a special tool, arrows are visible when looking from the top down, and hearts are visible from the bottom up. This pattern does not appear in other diamond shapes.
Ideal vs. Excellent Diamond Cut
Ideal is a superior cut grade to excellent cut. For Round Brilliant diamonds, Ideal + Hearts is the highest grade.
Can Lab-Grown Diamonds Be Graded on Cut?
Lab-grown diamonds can and should be graded on all 4Cs and certified. Lab-grown diamonds are cut and polished just like their mined counterparts. It is inadvisable to purchase any diamond without diamond certification.
Which Diamond Cut Holds Its Value?
Most diamond cuts should hold their value, but different diamond cuts will have different values. Diamond cut grades impact the total price of a diamond, so diamonds with a higher cut grade will be more valuable, and will also hold their value.
However, cut grade aside, certain types of diamond cuts are considered more valuable than others when used in specific diamond shapes. For example, a brilliant cut in a Round Brilliant cut diamond is the most sought-after diamond cut, and therefore the most expensive. Due to its ongoing popularity, Round Brilliant cut diamonds will always hold their value.
VRAI Created Diamonds: A Cut Above the Rest
VRAI created diamonds are cut to perfect proportions to reveal a superior, striking brilliance ranging from Ideal + Hearts to Ideal to Excellent. Each VRAI created diamond cut is the result of expert craftsmanship with exacting precision and unmatched standards for quality and sustainability. VRAI offers 30 different diamond shapes, including VRAI exclusive diamond cuts created by our master craftspeople and Cut for You.
Only VRAI created diamonds are certified carbon neutral. Our diamonds are grown in our zero-emission foundry. They are inspected more than 1,300 times, from the moment the diamond seed is placed into a reactor to the finished ring. Fewer than 1% of all diamonds on the market meet this high standard of quality.
Naturally, the exacting precision and craftsmanship of higher cut quality garners a higher price. But due to our vertically integrated supply chain and in-house production, our diamond prices are the most competitive in the industry. VRAI created diamonds offer the highest value for high cut quality diamonds.
Explore VRAI Created Diamond Cuts
Discover our full inventory of lab-grown diamonds featuring classic and signature diamond cuts crafted in our Cut for You process. All VRAI created diamonds feature a cut grade of Excellent of above, ensuring a beautiful and brilliant lab-grown diamond no matter the cut type.